UCSB Hist 133C, L
4:
Germany: 3 Empires, 4 Republics
by Prof. Marcuse, Jan. 12, 2004
(superceded by 2006 lecture)
What is Germany (Deutschland)?
- Administrative: return Q1, book probs?
textbook pages for Wed.: 13+25, 32f, 46f, 55-7, 67, 137f, 170, 180ff, 212ff,
247, 254, 282, 337f
Note what the acronyms mean and what the orientation of each party is. Q2
on Wed. will be based on these!
- What is a state? 2 principles
- 1st and 2nd Reichs: 800-1806, 1871-1918
- 1st and 2nd Republics: 1848-49, 1919-33
- 3rd Reich: 1933-45
- 3rd & 4th republics: 1949-1990: BRD/FRG & DDR/GDR
What is a "state"? Empire?
- Based on monarchy (dynasty)
- "L'etat, c'est moi" (Louis XIV; absolutism)
- Examples:
- Carolingians (Charlemagne)
- Bourbon, Hanover, Wittelsbach (Bavaria)
- Habsburg (Austria)
- Hohenzollern (Prussia)
- Empire: collection of kingdoms, etc.
- Emperor, German Kaiser (Caesar)
- Inherited, or elected
What is a "state" II
- Based on populace
- People control the gov't
- Have a body of common laws: constitution
- Elect representatives
- "Republic"
- Federal (German Bund), federation, confederation
First 2 Reichs
- (Holy) Roman Empire of the German Nation
- starts w/ Charlemagne's sons; ended by Napoleon
- 800-1806
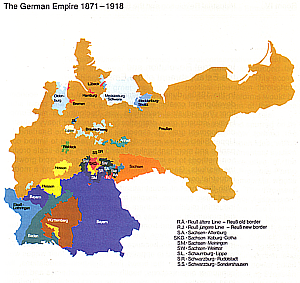
- Imperial Germany, 1871-1918
- started by Bismarck and William I (Hohenzollern)
- Bismarck united Germany in 3 wars
- ended with capitulation after "Great War" (WW1), Nov. 9, 1918: Kaiser
abdicated, republic proclaimed
Important Point: haphazard, contingent way that central Europe became
"Germany"
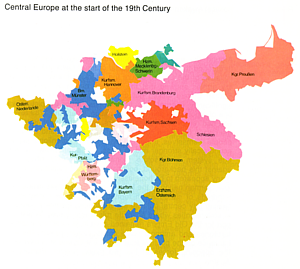
map of central Europe prior to 1806: conglomerate of 236 states, emperor
is elected |
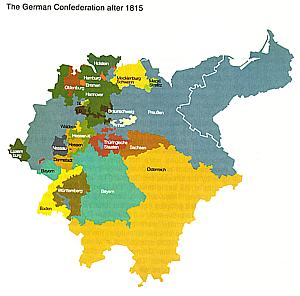
1819-1830: consolidation to 30 states |
Germany's 1848 Revolution
- Uprisings in Paris, Berlin, Vienna, Frankfurt
- Pre-parliament convened in Frankfurt
- Offers constitutional monarchy to FW IV
- Refuses "Never will I let a scrap of paper come between me and my people"
- Democrats driven out (Carl Schurz)
 |

Democrats being swept out of the German lands after the failure
of the 1848 revolutions.
(Compare to the 1928 DDP election poster, where right-wing rabble
is being scraped off the continent by a black-red-gold shield -
L5)
Friedrich Wilhelm IV doesn't accept the crown offered by the Frankfurt
Parliament
|
Bismarck's Reich (1871-1918)
- Bismarck unites German states "from above" (1848 democrats failed to do
it "from below")
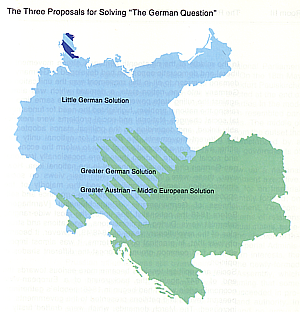
- Large, medium, small "solutions" to the "German question"
- Grossdeutschland: federal state (can accommodate greater diversity)
- Kleindeutschland: centralized state
- this prefigures the debate after 1945: W. Germany="federal" republic;
smaller E. Germany=centralized state
Important Changes in the 1890s: 1888 Wilhelm I dies, Frederick
III dies after 100 days, Wilhelm II becomes Kaiser

This 1913 poster praises the German social insurance system, which was
implemented by Bismarck to "take the wind out of the sails"
of the social democratic movement in the 1880s |
 |
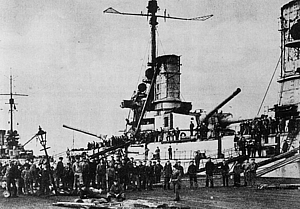
The sailors mutiny in Kiel on Nov. 6, 1918, triggering revolution and
initiating the end of World War I
1890: William II drops "pilot" Bismarck (famous
cartoon in satirical magazine Punch
|
What is "Germany"?
- dynastic states:
- Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation (with elected Kaiser; 1806=House
of Habsburg)
- Kaiserreich (emperor's empire) 1871; created by Bismarck; ruled by House
of Hohenzollern
- Third Reich (created by Hitler), 1938
- constitutional states (republics):
- 1848 National Convention
- 1918 Weimar Republic (constitution written there)
- 1949: Federal Republic of Germany (FRG); Bundesrepublik Deutschland (BRD)
- 1949: German Democratic Republic (GDR); Deutsche Demokratische Republik
(DDR)
page by H. Marcuse, prepared for web 1/18/04, updated 1/20/04, 1/12/06
back to top, to UCSB Hist 133c
homepage