UCSB
Hist 2c, L 12: World War I
by Prof. H. Marcuse, May 8, 2003
Question: How does WW1 fit
into world history?
- Events and causes
- Consequences
Textbook (Adler, World Civilizations)
chapter summary (p. 541)
The system erected by Bismarck
to keep France isolated and helpless broke down after the impetuous William
II took over the direction of foreign policy in Berlin. Within a decade, the
blocs that would contest WW1 had been formed. When a Serbian nationalist youth
assassinated the heir to the Austrian throne in 1914, a general war broke out
that, contrary to expectations, lasted for more than four years.The
battlefields where huge slaughters took place were matched in importance by
the home fronts, where governments intervened in unprecedented ways to spur
the civilian war effort. Women in particular were affected, as the desperate
need for labor impelled politicians in all countries to forget prewar restrictions
on female activity.
Preceding Events
- Decline of Ottoman Empire:
- power vacuum in Balkans
- 1908: Austria takes Bosnia
- 1912 Italy: Libya
- 1912-13 Balkan Wars
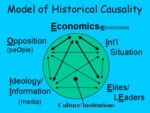 Model
of Causation in History
Model
of Causation in History
- Nationalism (idea/people): ethnic
and religious minorities in the Austro-Hung. and Ottoman empires
- Alliance system (int'l):
Triple Alliance (Germany, A-H, Italy)
Triple Entent (Britain, France, Russia)
- Economics
macro: colonial competition
micro: "primacy of domestic policy"
- Leadership/gov't: Bismarck vs.
William II
2 leaders, 2 paradigms
Otto v Bismarck (1815-1898) William
II (1859-1941)
"Little" events & their consequences
Arrest of Gavrilo Princip, 1914
World Trade Center, 2001
Course of WW1
- 1914: Schlieffen Plan for 2 front
war
- First defeat France, then
by train to Russian front
- Not "home by Christmas," but
stagnation
- Hindenburg's victories in
East (Tannenberg)
- 1915-16: huge casualties on Western
front
- 1917: Germany resumed submar.
warfare
- Russian revolutions in Feb.
and Oct.
- US entry into war in April
- Dec. last German offensive
- 1918: summer German retreat; Nov.
armistice
New type of warfare
- Supply system (railroads)
- total mobilization
- Machine guns (500-1000 rounds/minute)
- Tanks (Sept. 1916)
- Trenches
- Poison gas
- submarine (Lusitania, 5/15)
- aircraft
War casualty statistics
- Horses at start of war: Germany
715,000; A-H 600,000
- Verdun, from Feb. 1916: France
and Germany: over 1 mio. dead
- Sommes river, from June 1916
British lost 58,000 on first day (cf. Vietnam)
Total Allied: 600,000 by November
- Totals: A-H 90% of 7.8 mio=7mio
Russia: 76% of 12 mio=9.1 mio [4.9 wounded]
British Empire: 73% of 8.9 mio=6.1mio [4.2 w.]
France: 73% of 8.4mio=6.2 mio [3.6 w.]
Germany: 65% of 11 mio.=7.1 mio [3.6 w.]
US: 8% of 4.4mio=.32mio [.2 w]
Announcements
- Midterm evaluation (my
midterm)
help me to improve the rest of the course
- 2nd paper due date:
Thursday, May 15, 11am
(not 5/13)
- Rewrite due date: Tuesday, June
3, 11am
(not section the week before)
- New dates for CLAS workshops
lecture by H. Marcuse on 5/8/03;
outline prepared for web on 5/11/03.
back to top, to Hist 2c homepage
 Model
of Causation in History
Model
of Causation in History