| Standards
of Living Compared (back to top)
- What to compare: E. Germany vs. W, or vs. E. bloc?
Demographics: urbanization
1950: 29% in communities <2,000 in both E & W�1980: 6% in W,
24% in E�1950: 48% in town >10,000 in both E and W�1980: 74% of W
vs. 57% of E
overall pop: E 16.7 mio in 1939 and 1980 (18.4 in 1950)�W 43 mio in
1939, 61.7 mio. in 1980
Standard of living: how to measure
range of income disparity, social mobility
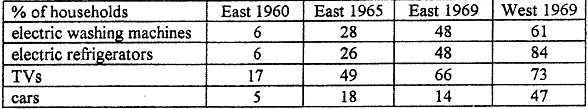
table of stats of consumer goods
Higher education: econ. and gender diversity
- What to compare: E. Germany vs. W, or vs. E. bloc?
Demographics: urbanization
1950: 29% in communities <2,000 in both E & W�1980: 6% in W,
24% in E�1950: 48% in town >10,000 in both E and W�1980: 74% of W
vs. 57% of E
overall pop: E 16.7 mio in 1939, 16.7 mio. 1980 (18.4 in 1950)�W 43
mio. in 1939, 61.7 mio. in 1980
- Higher education: economic and gender diversity�(stats: Fulbrook p.
231f)
E: 1950s- 50% working class (69% of pop.); 18% in 1967�W: 4% in 1950,
7.5% in 1970 (57% of pop.)
- Standard of Living
- How to measure it?
range of income disparity, social mobility
access to consumer goods
|