Hist 33D,
L 19: "Interdisciplinary Perspectives" (Concluding Lecture)
by Prof. H. Marcuse, UCSB, Dec. 2, 2003
[short version of Anne Frank lecture]
What did we learn in this course?
- Announcements: J7+8, final projects, LA$, 133q
- Anne Frank: more or less than the truth?
- Summing up
- course evaluations
- Return project printouts and discuss uploading and form of final projects
(handout)
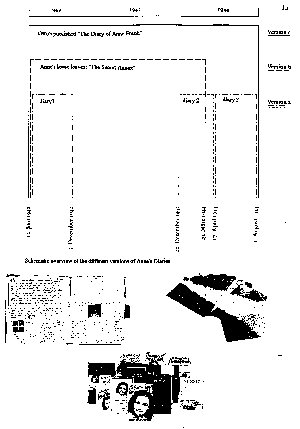
3 Basic Versions of Anne’s Diary
 |
 |
Schematic diagram of 3 basic versions of Anne Frank's diary
(from German translation of Critical Edition) |
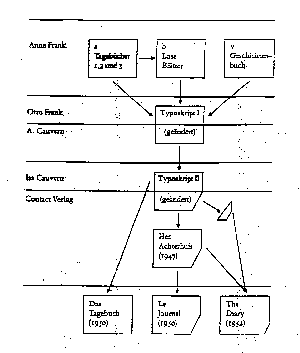
Flow chart showing the relationship between the various
early publications of Anne Frank's diary |
More versions, more audiences
- Dutch publisher (1947): T II - 15 deletions
- French translation (1950)
- German translation (1950): Typescript II
- English translation (1952): hybrid (7 back in)
- Critical edition (1986): versions a, b, c
- Definitive edition (1995)
- Miriam Pressler redoes 45-46 synthesis by Otto
- Stage versions (1955; 1997)
- Film versions (1959; 2002)
 Anne
Frank: Person vs. Symbol
Anne
Frank: Person vs. Symbol
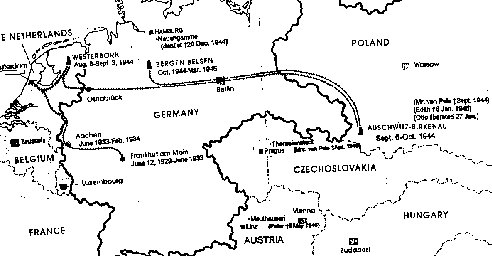
Anne (age 4), with mother Edith, and older sister Margot Frank, in Frankfurt
am Main (Germany--Anne's birthplace), January 1933
Contextualizing Anne Frank's Story (1929-1945)
Course Evaluations
- need a student to drop these at the history dept. after class (slide under
dept office door)
- I take these seriously, please give me your comments on the question sheet!
History (central points of this course!)
- Information is only as good as its source (applies to web pages,
too)
- Perspective is crucial
- Explain what is by where it came from
- issues of cause and effect, and
- distinguish preconditions, motivations, and goals
- examples:
- Hitler: role in the Holocaust
- 1920s: good or bad?
- 1930s, Kristallnacht
- euthanasia program; Auschwitz camp
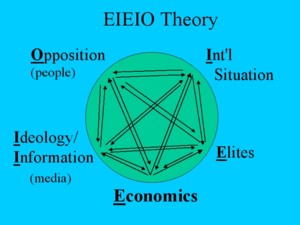 eieio
eieio
A model of historical causes
- Question:
What factors played a role in causing the Holocaust?
In allowing it to happen?
In general, what things play a role in allowing and making historical events
happen?
- Answer: 5 broad categories, interconnected:
- Economic factors (Marxism: these underlie all others)
- International factors (diplomacy, intervention)
- Elites (behavior of groups w/ special access to power)
- Ideology/Information/Media: perception of the world
- "Opposition": people, human agents
- "background" of culture and institutions
Psychology
- Human motivation
- Euthanasia doctors; Höss, Eichmann, Batt. 101
- Milgram experiments
- Distinguish:
- Preconditions
- Motivations
- Causes
- Goals (question of intent)
Roundup of (individual) Motivations
- racism (race-based antisemitism) (hate)
- ideological indoctrination (master race)
- obedience to orders (role of situation)
- deference to authority (bible: Abe vs. Sarah)
- careerism (preemptive obedience)
- conformity (peer pressure; solidarity)
- special selection of perpetrators
- wartime brutalization (situation)
- segmentation and routinization of task
- Economic / Int'l / Elite / Ideology / peOple
 Psychology
-> Sociology
Psychology
-> Sociology
- Collaboration and Jewish Resistance
- Judenrat and ghetto police
- German resistance: Context matters--the whole society
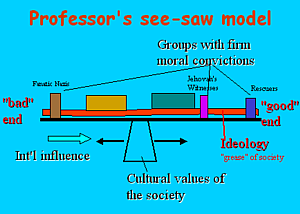
Professor's see-saw model of social dynamics: how does it apply?
Groups (Sociology)
- Denial: where it fits in
- Representations: Museums, fascism and art
Discussion of Final Projects: Getting them on the web
pass out project update handout and explain
prepared for web by H. Marcuse, Dec. 13, 2003, images added 12/14/03
back to top, Hist 33d homepage


 Anne
Frank: Person vs. Symbol
Anne
Frank: Person vs. Symbol  eieio
eieio Psychology
-> Sociology
Psychology
-> Sociology